Azure Blob
The Azure Storage connector can access both Azure Blob Storage and Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2, as they share the same underlying infrastructure. The key difference lies in whether Hierarchical Namespace (HNS) is enabled on the Storage Account. When HNS is enabled, the storage behaves like a Data Lake with true folder hierarchy, allowing for folder existence validation and persistent folder structures. Without HNS, the system treats folders as virtual paths within Blob Storage, meaning empty folders will not persist and folder existence cannot be validated. The same connector supports both configurations, automatically adapting to the Storage Account settings.
To create an Azure Blob endpoint:
Click Organizations.
Select an organization.
Click Endpoints.
Click the + Add Endpoint button.
Enter the name in the Endpoint Name * field.
Select Azure Blob from the Type * drop-down.
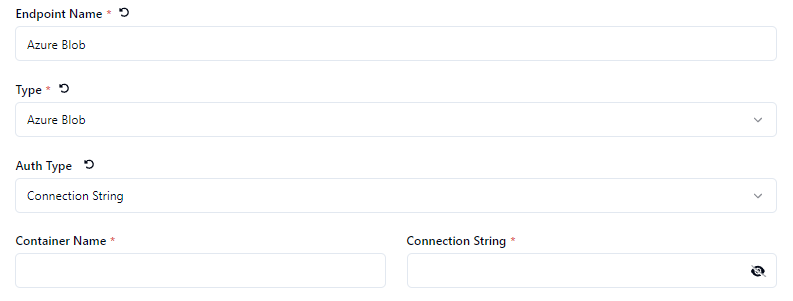
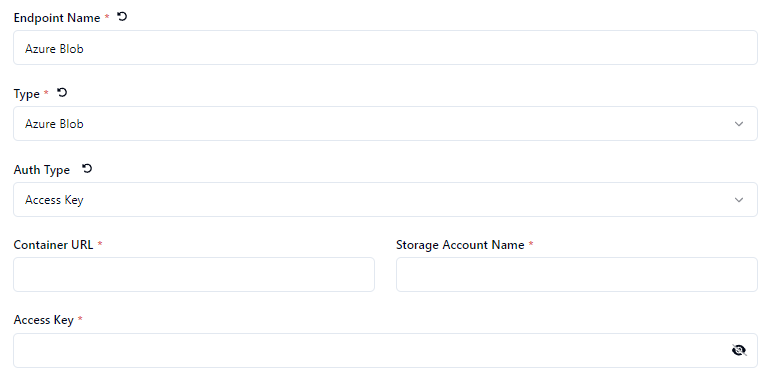
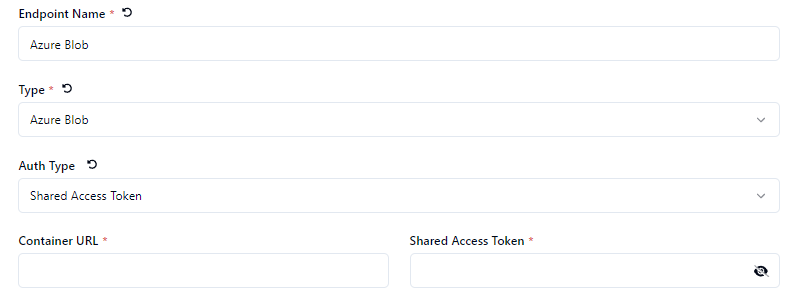
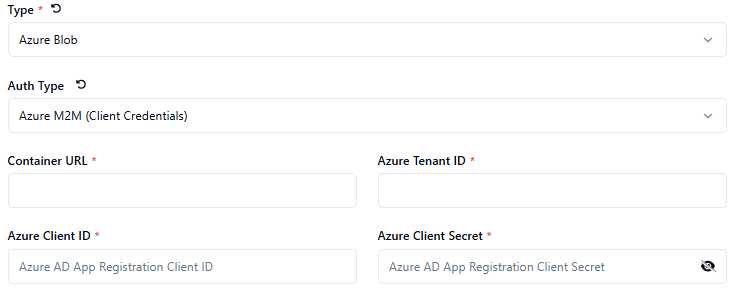
Choose the Auth Type - Connection String, Access Key or Share Access Token
Define the Container Name * or Container URL * depending on the Auth Type.
Define the Connection String *, Storage Account Name * or Shared Access Token * depending on the Auth Type.
Enter a description for the endpoint.
Click the Save button.
Connection String
Access Key
Share Access Token
External Identity Provider Authentication
Azure Machine/Client Credentials
External Identity Provider Authentication
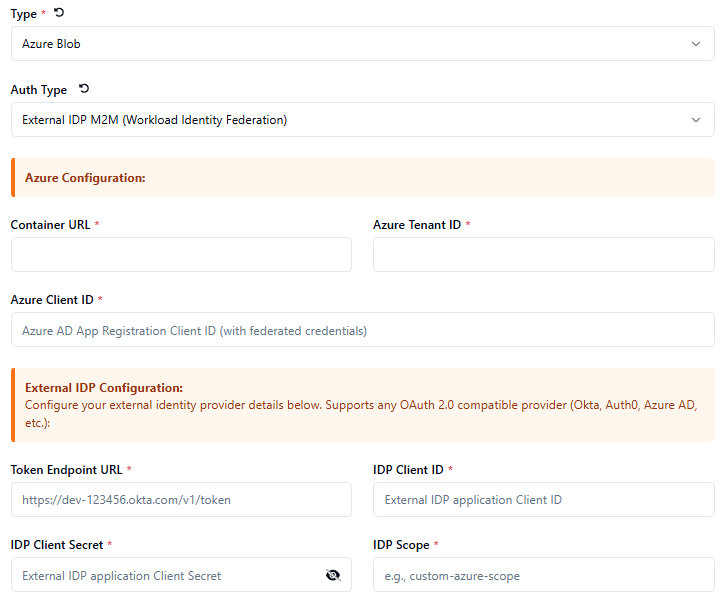
For more information see : Azure Blob - External Identity Provider Authentication
It's important to note that utilizing Thru's SaaS service for outbound connections might necessitate the whitelisting of our IP addresses by the respective target endpoints. This proactive step helps ensure seamless and secure communication, allowing our service to reliably interact with designated external systems and deliver optimal performance.
